AI and the Future of Work

As businesses see better ways to scale and grow, many are leveraging AI to do more with less—and it’s already delivering measurable results.
In 2024, Unilever used AI to streamline its processes, helping its Ice Cream division save up to 10% on raw materials, which is especially important for costly ingredients like vanilla and cocoa.
Likewise, Amazon already has plans to use generative AI to drive more same-day shipping with smarter robots.
The big players are moving fast. From streamlining processes to personalizing customer experiences, AI drives efficiency, innovation, and business competitiveness.
Companies that scale even just one strategic AI initiative are nearly 3x more likely to exceed ROI expectations. Yet only 8% of companies are scaling AI at an enterprise level and embedding the technology into core business strategy.
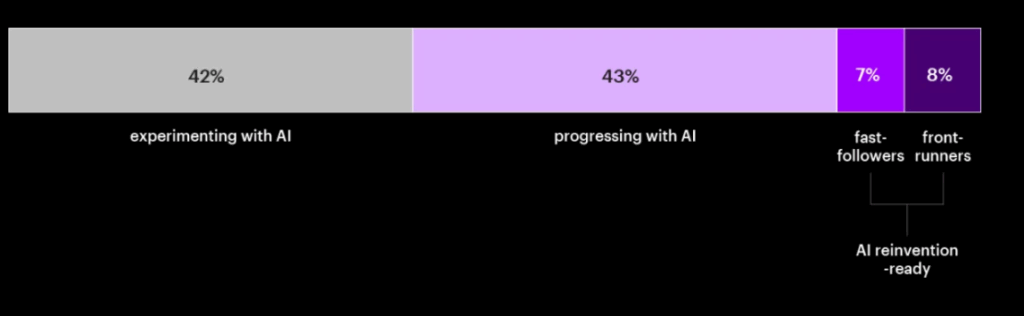
(Source: The Front-Running Guide to Scaling AI)
While AI is making waves, most companies have yet to move from experimentation to real, scalable impact.
For today’s business leaders, the question is a mix of urgency and opportunity: How can they prepare for AI in the workplace while staying focused on what matters most?
The conversation around AI and the future of work isn’t just about new technology. It’s about solving the right problems with the right support and delivering lasting value to people and organizations.
Why AI Is a Big Deal
AI is already changing the future of work, so now is the moment to take the lead. To seize this moment, leaders must understand why AI matters and what it demands in terms of vision, adaptability, and long-term strategy.
By 2030, McKinsey predicts that up to 30% of working hours in the U.S. could be automated, accelerating workforce transformation and pushing companies to rethink roles at an unprecedented pace.
Younger workers see the potential, too, with 51% telling Deloitte that generative AI will enhance their job efficiency, but they also express concern about transparency and leadership support.
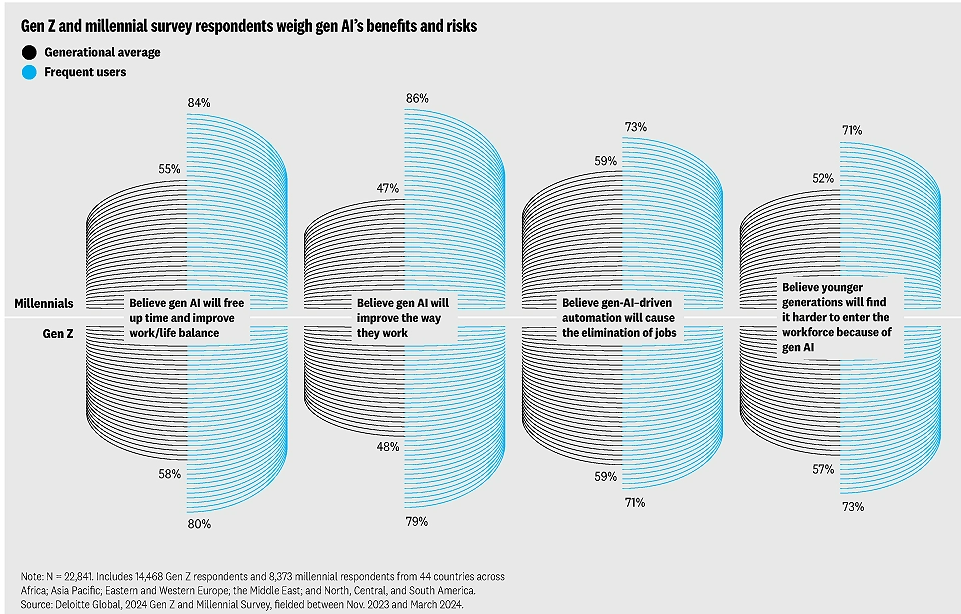
(Source: 2024 Gen Z and Millennial Survey)
This points to a need for organizations to not only adopt AI but also support cultural and structural shifts that make the transition smooth and inclusive.
The changes are only accelerating. As businesses begin to rely more on intelligent systems, the conversation isn’t just about capability; it’s about readiness. Understanding how AI is changing the future of work means understanding how quickly roles, responsibilities, and technologies are evolving.
What You Need to Make AI Work
Adopting AI is not about chasing trends—it’s about efficiency. AI’s true power lies in how it adapts to different sectors and solves your distinct problems. Many companies struggle not because they lack access to technology but because they don’t have a clear roadmap.
For effective AI implementations, businesses need to focus first on a problem AI can solve for them and then design a solution that’s flexible, scalable, and easy to use.
A Clear Problem to Solve: The most successful AI projects begin with a well-defined challenge. Whether it’s reducing manual work, improving customer engagement, or making better decisions, the “why” matters more than the “how.”
For example, Safeguard Properties, a leader in mortgage field services, faced inefficiencies with their property inspection process due to separate iOS and Android apps that lacked unity and modern functionality. Taazaa tackled inefficient property inspections by building an AI-powered mobile app. It unified iOS and Android platforms, used AI to analyze photos and verify checklists, and cut manual auditing by 50% while speeding up processing by 30%. This streamlined workflows, boosted accuracy, and saved time.
User-Centered Design: Even the smartest AI won’t succeed if it’s hard to use. Intuitive, human-centered experiences are critical for adoption and impact. This is where AI and human intelligence must work hand-in-hand, especially when systems are built to augment, not replace, the workforce.
Scalable, Flexible Tech: One-size-fits-all solutions rarely work in dynamic environments. Businesses need adaptable technology that grows with their goals and infrastructure.
Enlighten Mobility, a medical device company, needed a way to interface their AI-powered GMat device with users and securely manage test data. Taazaa developed the EDNA desktop app to capture and analyze sensor data, as well as a cloud-based web app to store reports and manage users. The solution scaled their AI capabilities from raw data to actionable insights.
AI Challenges Businesses Face
AI holds immense promise, but significant obstacles stand in the way. Here are things to consider:
Workforce disruption is a major concern. Employees may resist change due to fears of job loss or difficulties adapting to new tools, which can lower morale and productivity. Broader societal impacts loom, too. Over-reliance on AI could widen skill gaps, leaving less-experienced workers behind. For instance, if workers perceive AI as a threat rather than an aid, adoption stalls, and ROI is delayed.
Additionally, over-reliance on AI risks widening skill gaps, as less-experienced workers may lack access to upskilling, leaving them unprepared for evolving roles. This societal impact creates a cycle where companies face internal pushback and talent shortages, hindering effective AI integration.
Ethical concerns demand serious attention. Biases in algorithms can perpetuate inequities, while increased data usage raises privacy risks for individuals and organizations alike. A 2024 UNESCO study exposed troubling biases in Large Language Models (LLMs). It found these models often cast women in domestic roles—up to four times more frequently than men in one case—tying them to terms like “home,” “family,” and “kids,” while linking male names to “business,” “executive,” “pay,” and “career.” It also highlighted homophobia and racial stereotyping.
In 2023, the EEOC settled its first AI hiring bias lawsuit with iTutorGroup, which programmed its software to reject female applicants over 55 and males over 60, discriminating against over 200 candidates. The company paid $365,000 to settle, highlighting the risks of biased AI in hiring.
Similarly, Amazon’s 2018 AI hiring tool downgraded resumes with terms like “women’s” due to male-dominated training data. While a lawsuit was filed claiming discrimination against female applicants, Amazon settled it quietly, with no public admission of liability, and discontinued the tool.
Regulatory uncertainty only adds to the complexity. Laws around data privacy, security, and AI governance vary by region and are evolving rapidly, creating compliance challenges that can shift overnight.
Companies are starting to feel the pressure. Recent data shows that more organizations are now actively managing risks related to inaccuracy, cybersecurity, and intellectual property infringement. These are three of the most common gen AI-related risks that have already caused negative consequences for businesses.
Costs are another hurdle. Beyond the initial investment in AI technology, organizations must account for ongoing expenses: maintenance, training, system updates, and scaling. With technical complexity on the rise, internal teams often lack the time or expertise to build, integrate, and manage AI systems effectively. This leads to delays, inefficiencies, or abandoned initiatives.
Use This Checklist to Get Started with AI
Getting ready for AI in the workplace isn’t about a dramatic overhaul. It’s about building readiness, piece by piece.
If you’re exploring AI in your organization, here are a few ways to get started:
- Identify a business challenge that could benefit from automation or smarter insights.
- Engage stakeholders early to define success and user needs.
- Focus on usability and real-world outcomes—not just features.
- Work with a partner who can guide the process and adapt with you.
Will AI Replace Human Jobs?
Today, the big question is, “Will AI replace human jobs?” The answer is: Not entirely.
While some roles will be automated, new ones will emerge, and many existing roles will evolve.
The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Survey notes that between now and 2030, workers can expect that 39% of their current skill sets will be transformed or become outdated, highlighting the pace of change.
In the same survey, 63% of employers feel skill gaps are the biggest barrier to their business transformation.
The good news is that this gap is shrinking, and more employees than ever are engaging in reskilling and upskilling. At the same time, 85% of employers plan to prioritize upskilling, and 70% expect to hire for new skills.
Accenture’s Pulse of Change 2024 report reveals that 55% of employees say comprehensive training and clear guidelines on responsible use would boost their confidence in using gen AI tools, signaling a proactive shift toward reskilling to meet AI-driven demands.
However, the survey noted a visible disconnect between C-suite’s AI talent strategy and their employee’s ability to benefit from it.
AI and the future of work isn’t about replacing people. It’s about enhancing them with the AI tools they need to work more efficiently.
Businesses that invest in training, adaptability, and tech partnerships will be better positioned to lead through change.
Shape Your Future with AI
Incorporating AI into business operations should be a thoughtful, strategic, and human-centered process, with a clear problem to solve and a defined goal to reach.
If you’re having trouble implementing AI or are unsure how it can benefit your business, Taazaa can help. As an AI development company, we help bridge the gap between vision and execution.
At Taazaa, our design-first approach helps organizations clarify their ideas, reduce development risks, and move with confidence. We help teams go from concept to solution quickly, thoughtfully, and at the right scale. Contact us today!