Understanding the Different Mobile App Store Guidelines

App stores, led by giants Apple and Google, hold considerable sway over the fate of your app.
If the app violates store rules, it won’t be listed in the app store, making it harder for users to find and install it.
These rules are the backbone of the app store’s commitment to user security, experience, and quality assurance.
This article gives a brief overview of the five biggest app stores, then looks at the rules your app must adhere to if you want to market it in these stores.
Major Mobile App Stores
The top three app stores worldwide are the Google Play Store, Apple App Store, and Amazon Appstore. These three stores enjoy more than 85% of the app market share. Microsoft and Samsung also have their own stores, but Google, Apple, and Amazon are the titans.
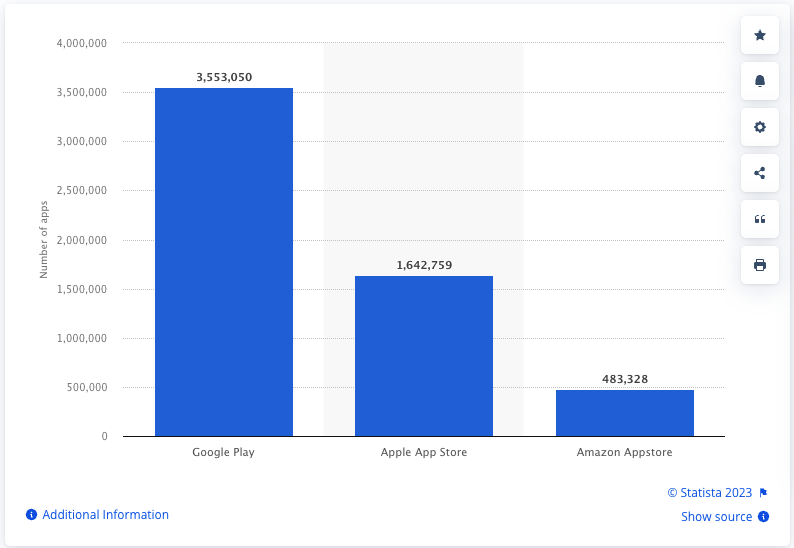
Image Credit: Statista
Google Play Store
The world’s largest app store is the Google Play Store. It’s the primary hub for Android devices. With its open ecosystem, it offers a more diverse range of apps and allows for greater customization for developers.
This flexibility also necessitates rigorous guidelines to prevent threats and ensure quality control. With its vast reach, especially in emerging markets, the Google Play Store is essential for developers aiming for global recognition.
Apple App Store
The exclusive gateway to iOS devices, the Apple App Store is known for its strict guidelines and thorough review process. Hosting millions of apps, it is second only to Google as one of the largest app platforms in the world.
Catering primarily to iPhones and iPads, the App Store is recognized for its premium user base and higher monetization opportunities. Its emphasis on design, user experience, and stringent privacy standards makes it a favored choice for many developers and users.
Amazon Appstore
Initially launched for the Amazon Fire tablets, the Amazon Appstore has since expanded to cater to a broader range of Android devices. While its size is considerably smaller than the Apple App Store and Google Play Store, it offers unique opportunities, especially for apps integrated with Amazon services or looking to tap into the Amazon ecosystem. Its guidelines emphasize user experience and integration with Amazon’s products and services.
Microsoft Store
The Microsoft Store was created as an app store for Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 to distribute Universal Windows Platform apps. With Windows 10, Microsoft merged its other distribution platforms into Microsoft Store, making it a unified distribution point for apps, console games, and digital videos.
Microsoft Store offers a unique ecosystem integrated closely with Microsoft’s suite of services. If you’re targeting enterprise solutions or Microsoft’s loyal user base, you may want to consider this platform.
Samsung Galaxy Store
Designed exclusively for Samsung devices, the Samsung Galaxy Store focuses on apps optimized for Samsung hardware, including smartphones, tablets, and wearables. Developers looking to leverage features unique to Samsung devices, such as the S-Pen or Samsung DeX, would benefit from this platform. The store emphasizes apps that provide enriched experiences tailored explicitly for Samsung users.
Google Play Store Guidelines
If you want to market your app to the broadest audience of Android users, the Google Play Store is the place to be. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its guidelines. The standard review process takes about three days. If the queue is long or the nature of your app requires a close review, the process may take up to seven days or longer.
Overview of Google’s Review Process
Submission: Developers upload their apps using the Google Play Console. This includes providing detailed metadata, APK files, and other relevant assets.
Automated Scans: After submission, the app undergoes automated scans by Google’s systems, checking for malware, policy violations, and major functionality issues.
Manual Review: Some apps are also subjected to a manual review, mainly if they’ve triggered any flags during the automated scans or if they belong to sensitive categories.
Feedback or Publication: Post review, developers are informed about the status. Approved apps get published, while rejected ones receive detailed feedback.
Key Areas of Focus
Content Guidelines: Google has a clear set of policies outlining permissible content. This includes restrictions on explicit content, hate speech, violence, and anything that promotes harmful behaviors.
App Quality: An app must meet Google’s performance, stability, and responsiveness standards. It should work across a range of devices and Android versions without significant issues.
Design: Google offers Material Design guidelines to help developers create intuitive and engaging user interfaces. While not strictly enforced, apps closely following these guidelines often provide better user experiences.
Technical Aspects: The app must be free from major bugs and crashes and handle user data responsibly.
Monetization and Ads: Google has guidelines on how apps can monetize. In-app purchases must use Google Play’s billing system. Advertisements must be clearly identifiable and not mimic the app’s UI or mislead users.
Privacy and Security Requirements: Apps must have clear privacy policies, inform users about data collection, and seek permissions appropriately. They should also avoid any unsafe practices that might compromise user data.
Common Reasons for App Rejection
Intellectual Property Violation: Using copyrighted material without permission or mimicking other apps can lead to rejections.
Misleading Claims: Apps that promise features they don’t deliver or present themselves falsely are likely to get flagged.
Inappropriate Content: Any app containing or promoting content that violates Google’s content guidelines is subject to rejection.
Unsafe Handling of User Data: Failure to adhere to privacy and security guidelines can lead to rejection, especially with an increased focus on user data protection.
Steps to Address a Rejected or Suspended App
Review the Feedback: Google provides detailed feedback for rejections. Analyze the reasons your app was rejected.
Make Necessary Changes: Address the issues highlighted in the feedback. This might involve fixing bugs, modifying content, or adjusting monetization strategies.
Resubmit: Once you’ve made the changes, you can resubmit the app for review. Ensure you’ve addressed all concerns to avoid subsequent rejections.
Appeal Process: If you believe your app was wrongly rejected, Google offers an appeal process. Here, you can provide further explanations or clarifications to support your case.
You can learn more about publishing your app from Google Play Store’s policy center. You can also find help in the Google Play Developer Community, a Google group where developers can discuss topics related to the Play Store.
Apple App Store Guidelines
Apple’s commitment to delivering a seamless and secure user experience has led to a rigorous app review process. Here’s a deeper dive into what this entails.
Overview of Apple’s Review Process
Submission: Developers submit their apps via Apple’s App Store Connect platform. The app, along with its metadata, is then queued for review.
Automated Tests: Initial tests are conducted to check for obvious issues, like malware or immediate crashes.
Human Review: Apple employs a team of reviewers who manually assess the app, ensuring it complies with the guidelines set out by Apple. This process checks the app’s functionality, design, content, and more.
Feedback or Approval: Once the review is completed, developers receive feedback. If the app is approved, it gets published on the App Store. If it’s rejected, reasons for the rejection are provided.
Key Areas of Focus
Content Appropriateness: Apple places a strong emphasis on curating a user-friendly environment. Apps containing adult content, hate speech, graphic violence, or anything deemed offensive or inappropriate are generally prohibited.
Technical Performance: An app should be stable and bug-free. Any app that frequently crashes, has major bugs, or doesn’t perform as advertised will likely face rejection.
Business Models: Apple has clear guidelines regarding monetization. In-app purchases must be processed using Apple’s in-app purchase system. Apps offering subscriptions have additional guidelines to follow. Moreover, the way ads are presented and the transparency about them are crucial.
Privacy Concerns: With its focus on user privacy, Apple ensures apps do not misuse or collect user data without proper consent. Apps must clearly detail their data collection and usage practices in their privacy policies, and they should seek user permission to access certain device functionalities or data.
Common Reasons for App Rejection
Incomplete Information: Apps that lack proper metadata, demo accounts, or other necessary information for the review process get rejected.
Low-Quality User Interface: Apple prioritizes user experience. Apps with poor UI/UX designs or not optimized for all devices might face issues.
Violating Apple’s Developer Code of Conduct: This can include issues like promoting harmful behavior, having hidden features, or misleading users.
Misuse of Platform Features: Apps must use platform features (like notifications or location services) as intended.
Tips for Navigating the Review Process
Detailed Documentation: Ensure all aspects of the app, especially features and functionalities, are well-documented. Include explanations for potentially confusing or controversial elements.
Test Rigorously: Before submission, test the app extensively for bugs, crashes, and performance issues.
Follow Apple’s Design Principles: Familiarize yourself with Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines and ensure your app aligns with them.
Stay Updated: Apple occasionally updates its guidelines. Regularly check for updates and modify your app accordingly.
Engage with Feedback: If your app gets rejected, engage constructively with the feedback. Address the highlighted concerns and seek clarity if needed.
Learn more from Apple App Store’s app review guidelines. You can also find help in the Apple Developer Forums, a space for developers to discuss Apple platforms, tools, and programming practices.
Amazon Appstore Guidelines
Amazon Appstore plays a pivotal role, especially for developers aiming to tap into Amazon’s ecosystem, including Fire tablets and Fire TV. Understanding its guidelines ensures better integration with Amazon services and a smoother review process.
Overview of Amazon’s Review Process
Submission: Developers use the Amazon Developer Console to upload their apps, accompanied by necessary metadata, APKs, and other assets.
Preliminary Checks: Automated systems conduct initial checks for immediate issues like malware or stark policy violations.
Manual Review: Amazon’s team assesses the app manually, scrutinizing its content, functionality, and compliance with the guidelines. This helps ensure quality and compatibility, especially with Amazon devices.
Feedback and Deployment: The app goes live on the Appstore if approved. If rejected, developers receive specific feedback to guide corrections.
Focus Areas
Content Standards: The Amazon Appstore is a family-friendly platform. Apps containing explicit content, hate speech, or promoting harmful behaviors are typically not approved. Developers should ensure their apps are appropriate for a broad audience, including children, unless otherwise specified.
App Quality and Technical Requirements:
- Device Compatibility: Amazon emphasizes compatibility, especially with Fire tablets and Fire TVs. Apps should be optimized for various screen sizes and resolutions.
- Performance: The app should be free from critical bugs or crashes and demonstrate fluid functionality and responsive design.
- Amazon-specific Features: If an app integrates with unique Amazon services, such as Amazon In-App Purchasing, it must adhere to the specific guidelines and ensure smooth integration.
Monetization Rules: Like other platforms, Amazon has its billing system for in-app purchases. Apps should integrate this system for any transactions. Moreover, ads should be user-friendly, not invasive, and should not mimic the platform UI.
Data Privacy and Permissions: Apps must respect user privacy. This entails having clear privacy policies, informing users about data collection practices, and seeking necessary permissions transparently. Invasive data collection or vague permissions can lead to rejections.
Recommendations for Successful Submissions
Understand the Amazon Ecosystem: Familiarize yourself with Amazon devices and services. Ensuring compatibility and optimization for these devices can enhance approval chances.
Follow Amazon’s Design Principles: While not as stringent as Apple’s, Amazon does provide design recommendations. Adhering to these can improve user experience and app reception.
Detailed Documentation: Any unique features or functionalities, especially those integrating with Amazon services, should be well-documented. This can expedite the review process.
Engage with Feedback: If faced with rejection, understand the feedback and engage with it constructively. Address the concerns before resubmission to enhance approval chances.
Stay Updated: Amazon occasionally revises its guidelines. Regularly checking for updates and adapting accordingly can prevent unexpected rejections.
You can learn more from Amazon Appstore’s app submission FAQs. Amazon Developer Community is a good place to discuss the development of Amazon devices and services.
Microsoft and Samsung Guidelines
Given the limited appeal of these two app stores, we won’t spend a lot of time detailing their rules and guidelines. If you need to list your app in the Microsoft Store, they have a list of helpful guidelines. Samsung has also published their app distribution guidelines for developers.
Key Takeaways and Best Practices
As we wrap up our deep dive into various app store guidelines, here are the primary takeaways and best practices every developer should keep in mind.
Regularly Review Rules and Guidelines
App stores periodically update their guidelines. Regularly check official documentation, sign up for developer newsletters, and engage with developer communities to keep abreast of changes.
It’s also a good practice to schedule periodic guidelines reviews to ensure compliance, especially before significant app updates
Rule changes can be frustrating. It helps to view updated guidelines not as hurdles but as opportunities to improve your app for users and align more closely with platform standards.
Prioritize User Safety and Security
Implement robust security protocols tonsure your app is free from vulnerabilities that could compromise user data. Regularly test and update security measures.
Review permissions and only request necessary permissions, making sure to justify each one clearly to the user.
Stay updated on global privacy laws, as well. From GDPR in Europe to CCPA in California, it’s essential to understand and comply with the international privacy regulations that might impact your users.
Ensure High-Quality Performance and Functionality
With a multitude of devices available and new versions released each year, it’s crucial to regularly test and optimize your app for different screen sizes, resolutions, and operating systems.
Use app reviews, user feedback, and analytics to identify areas of improvement, too. Analyzing user feedback can often tell you what features or fixes your users want.
Many apps get rejected for similar reasons, such as crashes, slow performance, or misleading functionalities. Ensure your app isn’t falling into these common traps.
Be Transparent with Monetization and Data Practices
If your app includes in-app purchases, ads, or any other monetization method, make it transparent to users. Avoid hidden charges or deceptive practices; they can get you rejected or banned from an app store.
Clearly communicate how you collect, store, and use customer data. Ensure you have a transparent privacy policy that’s easily accessible and understandable.
Regularly update your users on changes to your monetization or data practices. Keeping an open line of communication helps build trust.
Guidelines Are Challenging
App stores are digital gatekeepers, ensuring that the apps reaching users’ devices meet specific standards of quality, safety, and integrity.
While they might seem intricate or daunting, they reflect a shared commitment to creating a great user experience.
Navigating these guidelines effectively involves a blend of technical expertise, ethical responsibility, and strategic foresight. Marketing your app in more than one app store can greatly increase the complexity and challenges.
An experienced mobile app development company can help you if your run into roadblocks or just want to hand off development to people who’ve navigated the maze before.